Hello friends, in this article I will discuss one of the fundamentals of flutter, namely programming darts. Especially the notion of data types and their variants. Let's kuy.
Definition
In dart programming languages (not darts anyway), data types are used to describe a description of a value or value (not necessarily a number, you know). There are many kinds of data types. So, before we go to the next stage. Let's make preparations first.
Preparation
- Open dartpad.dev
- And immediately practice there.
Variable
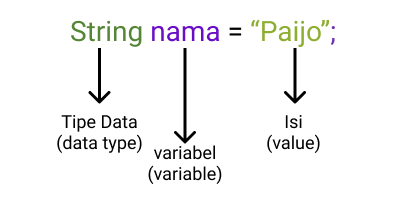
Before entering the data types. We must understand what a variable is. variable is a value or value that can be called again. Look at the image below
Cheat Seet
| Strings | Text |
| int | A non-decimal number |
| num | Number |
| double | Decimal number |
| dynamic | Can be text, numbers, or other objects |
| Lists | Stack data with keys as integer numbers |
| Map | Your own set of contents and keys |
| Objects | Is the base class of all objects in dart |
| bool | Truth data, contains true and false |
| var | This data type is used to declare the Object of the variable called |
| finals | final describes that a variable is only settered once and cannot be changed again. |
| const | It is short for constant, which means it cannot change. |
| Future | Is a data type that represents a function asynchronous |
| Functions | Is the data type used to send callback |
Data Type
As I said before, there are many kinds of data types, here are the types of data types.
1. Strings
A string is a collection of letters, numbers, and other punctuation marks. So the contents are free as long as the writing.
example:
void main() {
String data = "Hello World!";
print(data);
}
So, if you run it, it will produce the text
Hello world!
2. integers
integer is a data type that represents a number without decimals. The way of writing is as follows:
int a = 10;
o yes we can use print() to output the console. And so that dartpad can run the code, you need to create a main() method. So here's an example,
void main() {
int a = 10;
print(a);
}
The code above will output the number 10 if you run it. Well, if you don't believe that integer is not a decimal number, you can try changing it to int a = 10.5; Then the result will be an error.
3. num
num is an integer or floating point number. This data typecan be an integer or a double. Example of writing
void main() {
numdata = 20;
print(data);
}
This will return a number
20
But note, num cannot convert decimal numbers perfectly.
case example:
void main() {
num a = 0.1;
numb = 0.2;
num c = a+b;
print(c);
}
What do you think the result will be? 0.3? Yep, the result is
0.30000000000000004
lol. This is the uniqueness of floating numbers. So if you write something, please be careful and don't forget to round it.
4. double
double is a decimal number. Example of writing:
void main() {
double a = 0.1;
print(a);
}
0.30000000000000004
5. dynamic
dynamic is a data type whose contents can change, dynamic can be an integer, string, double, num, object, and so on. To prove that this variable can change, you can try running this code on dartpad.dev
void main() {
dynamica = 0.1;
a = "Hello World!";
print(a);
}
Then there will be no error, and will issue a console like this:
Hello World!
6. List
List is a stack of data. If you are familiar with PHP or Javascript , a List is an Array.
The data content of a List can be described statically, for example List<double>, List<String>, List<int> , and whatever else.
If you don't declare the data type of the contents of the List, the result will be List<dynamic>.
Example of writing List
void main() {
List data = [1,2,3,"a","b", "c"];
print(data);
}
Then the console result will be:
[1, 2, 3, a, b, c]
List, has a key (key) to fetch specific data. If you want to get the number 3 from the List that I have given as an example, then you need a key to retrieve the data.
Example how to take the number 3:
void main() {
List data = [1,2,3,"a","b", "c"];
print(data[2]);
}
why is the key the number 2? because the calculation of key in the list starts from the number 0. Go ahead and tinker with dartpad, OK?
below is an explanation of the key and the contents of the list above
0 = 1
1 = 2
2 = 3
3 = "a"
4 = "b"
5 = "c"
7. Folders
If you understand Javascript Object Notation (JSON), then it will be easier for you to understand what a Map is. Map is a key and content pair. These keys and contents are usually called key and value. Each key and value can be declared with a data type. For example
Map<String, dynamic>
from the example above, it can be interpreted that the key has a String data type, and the value has a dynamic data type.
Example of writing:
void main() {
Map<String, dynamic> data = {
"url": "https://gepcode.com",
"domain": "gepcode.com",
"author": "Gilang Pratama",
"totalAdmin": 1,
"supportSeo": 100,
};
print(data);
}
Well, the console output is as follows:
{url: https://gepcode.com, domain: gepcode.com, author: Gilang Pratama, totalAdmin: 1, supportSeo: 100}
How do I retrieve one of the values from the Map?
this is an example
void main() {
Map<String, dynamic> data = {
"url": "https://gepcode.com",
"domain": "gepcode.com",
"author": "Gilang Pratama",
"totalAdmin": 1,
"supportSeo": 100,
};
print(data["domain"]);
}
Well, the console output is as follows:
gepcode.com
8. Objects
This is the base class of all objects in dart
writing example:
void main() {
Object object = "Author";
print(object);
}
The result
Author
Next is the Object from class. We can write a constructor for initialize its contents. Example:
void main() {
Author Person = Person("Gilang Pratama", 27);
print(author);
print(author.name);
print(author.age);
}
class Person{
String name;
int age;
Person(this.name, this.age);
}
The result is
Instance of 'Person'
Gilang Pratama
27
9. bool
This data type contains truth.
writing example:
void main() {
bool data = true;
print(data);
}
The result
true
10. var
var is the data type used to declare the Object of the variable being called.
example of writing
void main() {
var author = Person("Gilang Pratama", 27);
print(author);
print(author.name);
print(author.age);
}
class Person{
String name;
int age;
Person(this.name, this.age);
}
The result is
Instance of 'Person'
Gilang Pratama
27
11. final
final describes that a variable is only settered once and cannot be changed again.
Example of writing:
void main() {
final data = "hello";
print(data);
}
The result is
hello
Prove if you can't change:
Example of writing:
void main() {
final data = "hello";
data = "world";
print(data);
}
The result is error.
The final variable 'data' can only be set once.
final is very useful for saving ram. So, don't forget it.
12. const
As the name suggests, const is short for constant, which means it can't change. Similar to final, but const is a deeper level than final.
Example of writing:
void main() {
final data = "hello";
print(data);
}
The result is
hello
Prove if you can't change:
Example of writing:
void main() {
final data = "hello";
data = "world";
print(data);
}
The result is error.
Constant variables can't be assigned a value.
This const is also very useful for saving RAM.
13. Future
Future is used in the use of asynchronous programming.
Example of writing:
void main() async {
print(wait data);
}
Future get data async{
return "Hello world";
}
The result is
Hello world
14. Functions
Function is the data type used for callback
writing example:
void main() {
searchBudi("Unfortunate", (available){
print(any);
});
searchBudi("Banyuwangi", (available){
print(any);
});
}
void searchBudi(String location, void Function(String exists) search){
if(location=="Banyuwangi") search("There is");
else search("None");
}
The result is
No
There is